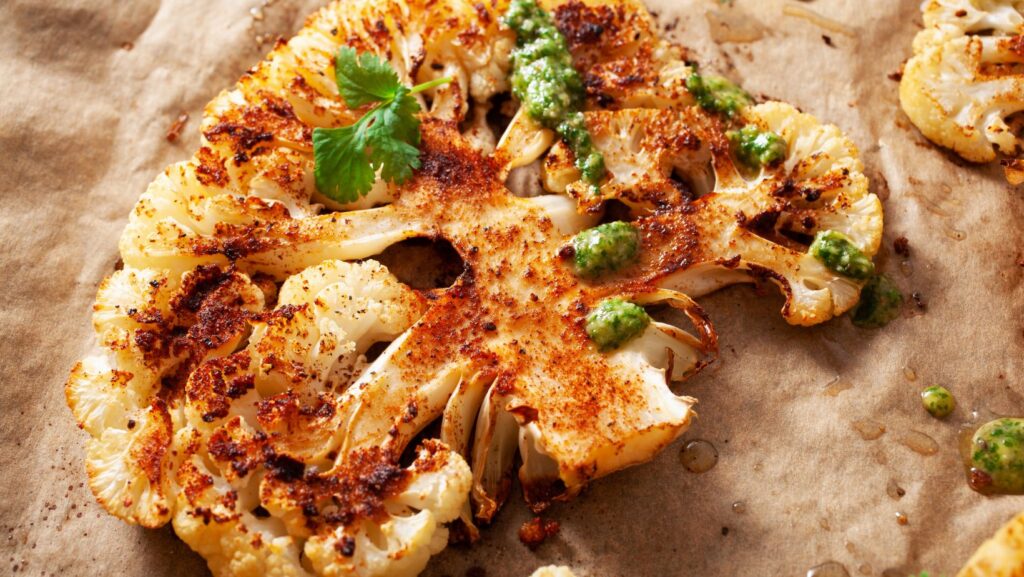
In recent years, plant-based meats have surged in popularity, promising a healthier and more sustainable alternative to traditional animal meats. As consumers increasingly lean towards vegetarian and vegan diets, the question arises: Is plant-based meat truly healthy? This query has sparked debates among nutritionists, environmentalists, and food lovers alike.
Is Plant Based Meat Healthy
Understanding plant-based meat involves examining its composition and how it differs from traditional animal meats. Plant-based meats are crafted from various plant sources, including soy, peas, and beans, designed to mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of animal meat. These alternatives often incorporate ingredients like beet juice to replicate the ‘bleed’ of real meat, along with vegetable proteins and fats to achieve the desired mouthfeel and flavor. Nutritionally, plant-based meats tend to be high in fiber and lower in cholesterol, providing a different nutritional profile from their animal-based counterparts. Manufacturers also fortify these products with essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron and vitamin B12, to closely match the nutritional benefits of animal meats. Yet, it’s crucial to consider the processing involved in creating plant-based meats, as high levels of sodium and additives can be present to enhance taste and shelf life, impacting overall healthiness.
Nutritional Profile of Plant-Based Meats
The nutritional profile of plant-based meats showcases a diverse array of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. Typically, these products contain high levels of protein sourced from plants like soy, peas, and beans, making them excellent alternatives for those seeking to reduce animal protein intake. They’re often rich in fiber, a nutrient absent in animal meats, which aids in digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness. Additionally, plant-based meats are usually low in cholesterol and saturated fats, contributing to better heart health.
Manufacturers frequently fortify plant-based meats with nutrients that vegetarians and vegans might miss, such as vitamin B12 and iron, enhancing their nutritional value. However, consumers should be aware of their sodium content and the presence of additives. High sodium levels can lead to increased blood pressure, while additives may raise concerns for those seeking whole, minimally processed foods. Thus, reading labels and choosing less processed options becomes paramount for health-conscious individuals incorporating plant-based meats into their diets.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Meat
Plant-based meats deliver multiple health benefits, aligning well with a balanced diet. First, they offer a high protein content comparable to that of animal meats, essential for muscle repair and growth. Second, their fiber content, absent in animal meats, enhances digestive health and aids in weight management. Plant-based meats also contain a variety of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health. They are typically lower in cholesterol and saturated fats, reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, many options are fortified with vitamin B12 and iron, nutrients often lacking in vegetarian diets. Consumers choosing plant-based meats not only embrace a healthier lifestyle but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
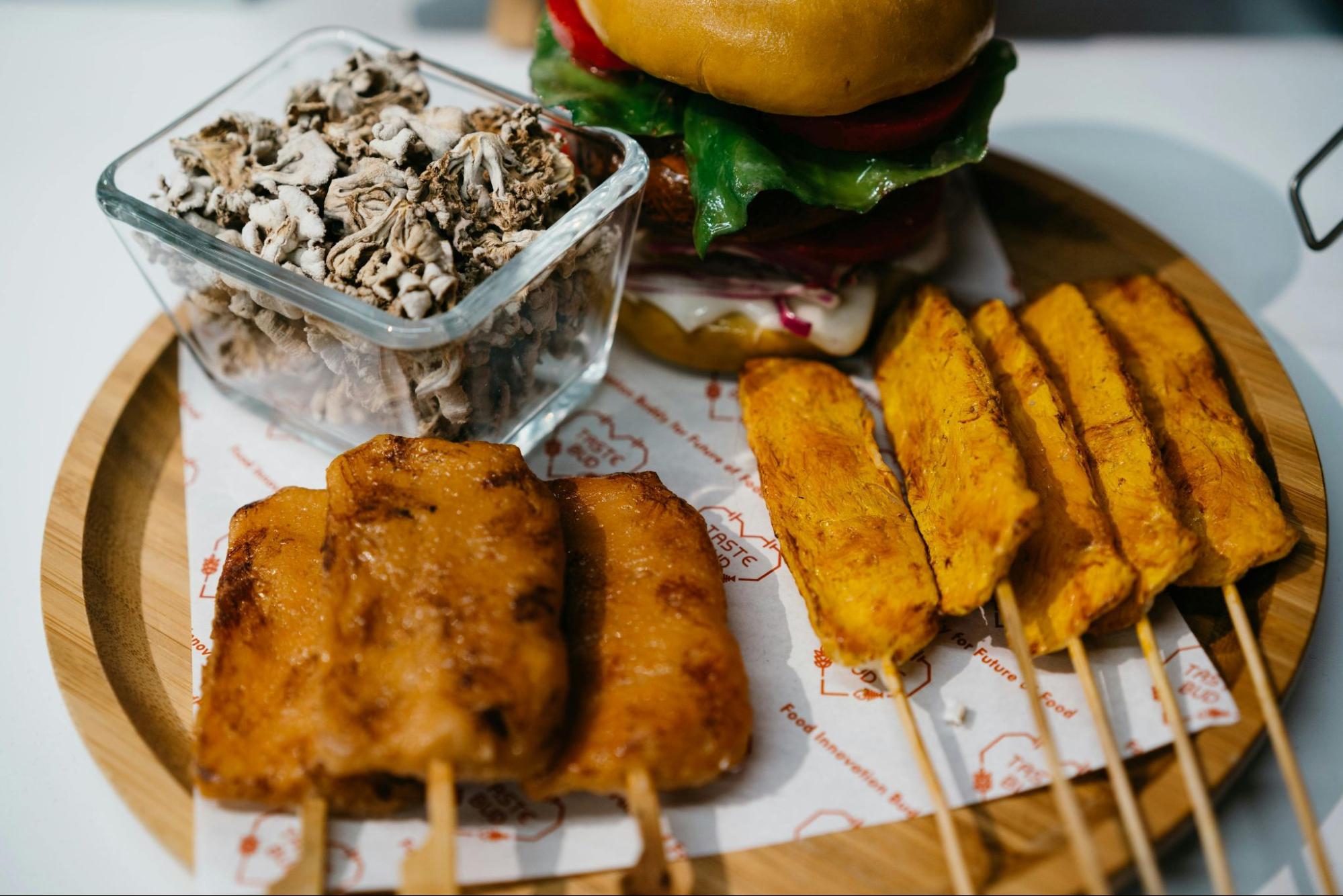

Potential Drawbacks
While plant-based meats present numerous health benefits, they also come with potential drawbacks worth noting. One primary concern involves their high sodium content. To enhance flavor and preserve shelf life, manufacturers often add significant amounts of salt, which can lead to elevated blood pressure when consumed excessively. Additionally, these products may contain processed ingredients, including additives and fillers, to mimic the texture and taste of animal meat. Such processing can result in a reduction of whole food benefits, making some plant-based meats less ideal for those prioritizing minimally processed diets. Lastly, while lower in saturated fats compared to their animal counterparts, certain plant-based meats might still incorporate coconut oil or palm oil, which are high in saturated fat, potentially impacting heart health if consumed in large quantities.
How to Incorporate Plant-Based Meat into Your Diet
Navigating the world of plant-based meats means balancing their nutritional benefits with potential drawbacks. They’re a great source of protein, fiber, and essential nutrients, offering a sustainable alternative to animal products. Yet, it’s essential to keep an eye on their sodium content, the presence of processed ingredients, and saturated fats. To make the most out of plant-based meats, moderation is key. Opting for versions with minimal processed additives and pairing them with whole foods can enhance your diet without compromising on health. As with any dietary choice, variety and balance are crucial. Plant-based meats can be a valuable part of a well-rounded diet when consumed thoughtfully, keeping their limitations in mind.