After undergoing surgery, patients are often focused on the prospect of recovery and returning to their normal lives. However, the recovery process can come with its own set of challenges, including potential complications that can affect one’s health and prolong the healing period. Understanding these complications is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure a smooth and safe recovery. Know that to be able to provide proper care, healthcare providers must present themselves clean, so it is important to learn how to properly wash scrubs, check Poppy Scrubs.
This article aims to shed light on some common post-surgical complications, providing essential information on how to identify, manage, and prevent them. By being informed, patients can better communicate with their healthcare team and take proactive steps towards their own health and wellness.
-
Infection
Infection is one of the most common risks associated with any type of surgery. It can manifest at the incision site or internally within the body. Signs to watch out for include unusual redness, swelling, or warmth at the surgical site, discharge that may be pus-like, and a fever exceeding 100.4°F (38°C). To prevent infection, it is vital to keep the surgical area clean and dry, adhere strictly to the wound care instructions provided by the healthcare team, and ensure all dressing changes are done using sterile techniques. If any signs of infection are noticed, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider immediately for appropriate management, which may include antibiotics or additional surgical intervention.
-
Post-operative Cognitive Dysfunction
Post-operative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a lesser-known but significant complication that primarily affects elderly patients, though it can occur in younger individuals as well. POCD can manifest as confusion, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be distressing for both the patient and their family. Nurses, particularly those enrolled in CCNE accredited online nursing programs like an RN to MSN – Adult Gerontology Nurse Practitioner program, play a pivotal role in identifying these symptoms early.
They are trained to observe changes in a patient’s mental status through regular interactions and assessments. By monitoring patients closely, nurses can detect early signs of cognitive decline and communicate these findings to the attending physicians. Early detection is crucial as it allows for the timely management of symptoms, potentially minimizing long-term impacts.
-
Bleeding
Bleeding after surgery can range from normal post-operative drainage to critical hemorrhaging that requires immediate attention. It is important for patients and caregivers to know the difference between normal and excessive bleeding. Signs of concerning bleeding include a rapid soak through of surgical dressings, unusually dark or continuous blood flow, and dizziness or weakness which could indicate significant blood loss. Patients should be instructed to monitor their wound for unexpected changes and report these to their healthcare provider. In severe bleeding, immediate medical intervention is necessary to prevent further complications.
-
Thrombosis
Thrombosis, the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel, can occur after surgery, particularly in patients who are immobile for long periods. If the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism. To prevent thrombosis, it’s crucial to get moving as soon as possible after surgery. Healthcare providers often recommend leg exercises, walking, and sometimes prescribe blood thinners. Signs of a possible blood clot include swelling and redness in the legs. Early detection and treatment are vital and can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications.
-
Pulmonary Complications
Pulmonary complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis (collapse of part of the lung) are significant risks after surgery, especially in patients who are not mobile or are already suffering from respiratory issues. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, chest pain, coughing, and abnormal breath sounds. One of the most effective ways to prevent these issues is through early mobilization and the use of incentive spirometry, which encourages deep breathing and keeps the lungs clear. Patients should also practice coughing and deep breathing exercises several times a day to maintain pulmonary function and prevent fluid accumulation in the lungs.
If symptoms of pulmonary complications arise, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to manage these conditions effectively.
-
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention, the inability to empty the bladder completely, can occur as a result of anesthesia or due to the type of surgical procedure. Symptoms include discomfort in the lower abdomen, swelling of the bladder, and difficulty urinating. This condition can increase the risk of urinary tract infections and can be quite uncomfortable. Patients experiencing signs of urinary retention should be encouraged to attempt urination at regular intervals and may need to be catheterized if natural urination is not possible. Keeping hydrated and walking can also help in reducing this risk. It’s important for healthcare providers to monitor urine output post-surgery to address this issue promptly.
-
Nausea and Vomiting
Postoperative nausea and vomiting are common complications that can extend hospital stays and increase discomfort for patients. Causes include the type of anesthesia used, the surgical procedure itself, and individual susceptibility. To manage this, healthcare providers often administer anti-nausea medication before and after surgery as a preventive measure. Patients are advised to avoid heavy meals and instead eat small, light, and bland foods as they recover. Hydration is also crucial, but it should be done slowly and steadily. If nausea and vomiting persist, additional medications may be necessary to control these symptoms effectively.
-
Constipation
Constipation post-surgery is a frequent issue due to limited physical activity, use of pain medications (especially opioids), and changes in diet. Symptoms include infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stool, and abdominal pain. To prevent constipation, patients should consume a high-fiber diet, stay hydrated, and move around as much as possible. Stool softeners or mild laxatives may also be prescribed by healthcare providers to facilitate bowel movements. Regular monitoring of bowel function is important, and patients should report any significant changes or discomforts to their healthcare team.
-
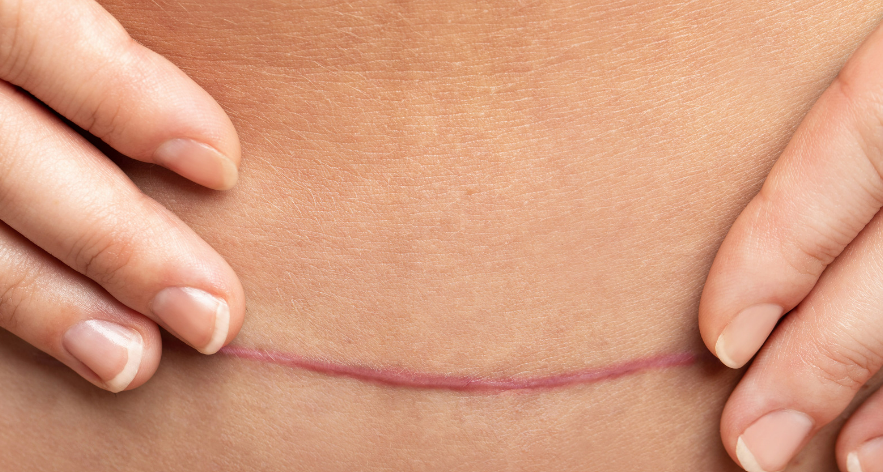
Scarring
Scarring is an inevitable aspect of surgery, as it is part of the body’s natural healing process. The appearance and severity of scars can vary based on the surgical method, the site of the surgery, individual healing processes, and proper wound care.

Minimizing scarring involves keeping the wound clean, avoiding direct sunlight on the area, and using recommended ointments or treatments prescribed by healthcare providers. For patients concerned about the aesthetic impact of scarring, options such as silicone sheets, steroids, or laser therapy may be discussed post-recovery to improve the appearance of scars.
Conclusion
Awareness of common post-surgical complications is crucial for a successful recovery. This knowledge empowers patients to take an active role in their postoperative care, facilitating better outcomes and reducing the likelihood of adverse effects. It’s important for patients to maintain open lines of communication with their healthcare team, reporting any new symptoms or concerns immediately. Recovery from surgery is a gradual process that requires patience, compliance with medical advice, and self-care. By understanding and preparing for these potential complications, patients can more effectively navigate the recovery process and return to their normal activities with confidence and health.