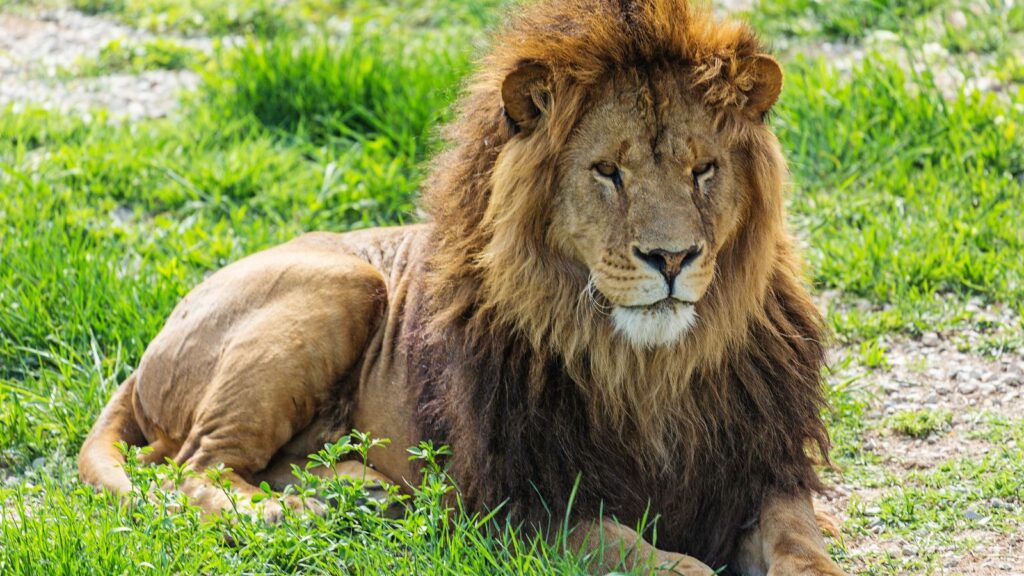
The lion, often dubbed the “king of the jungle,” captivates with its majestic presence and commanding roar. As one of the most iconic animals in the world, lions have fascinated humans for centuries, symbolizing strength, courage, and nobility. Found primarily in the grasslands and savannas of Africa, these powerful predators play a crucial role in their ecosystems.
Animal:H8n1113fyde= Loin
 Lions, members of the Panthera genus, are large felines recognized for their social structures. They live in prides, which include related females and their offspring and a small group of males. Weighing up to 420 pounds, male lions are larger than females, who weigh around 280 pounds.
Lions, members of the Panthera genus, are large felines recognized for their social structures. They live in prides, which include related females and their offspring and a small group of males. Weighing up to 420 pounds, male lions are larger than females, who weigh around 280 pounds.
The lion’s physique is built for strength and speed. Its retractable claws aid hunting, while its keen eyesight helps detect prey during twilight hours. A lion’s roar, audible up to 5 miles, supports territorial communication.
In terms of diet, lions primarily hunt large ungulates such as zebras and wildebeests. Prides collaborate during hunts, with females often leading the pursuit. This cooperative behavior increases hunting success rates, ensuring the pride’s sustenance.
Lions inhabit territories ranging from 40 to 400 square miles, dependent on prey density. Their presence influences the ecosystem, controlling herbivore populations and enabling biodiversity. Despite this ecological importance, lions face declining numbers due to poaching and habitat encroachment.
Physical Characteristics Of Lions
Lions stand as a symbol of power with their distinctive physical traits. These large felines possess unique adaptations that support their role as apex predators.
 Male lions measure up to 10 feet long, including the tail, and stand about 4 feet tall at the shoulder. Their weight can reach 420 pounds, while females weigh around 280 pounds. Males boast a majestic mane that varies from light blond to black, creating a striking appearance and indicating maturity. Both sexes have a muscular build, aiding their predatory prowess. Golden fur provides camouflage in dry grasslands, enhancing their stealth.
Male lions measure up to 10 feet long, including the tail, and stand about 4 feet tall at the shoulder. Their weight can reach 420 pounds, while females weigh around 280 pounds. Males boast a majestic mane that varies from light blond to black, creating a striking appearance and indicating maturity. Both sexes have a muscular build, aiding their predatory prowess. Golden fur provides camouflage in dry grasslands, enhancing their stealth.
Lions showcase several hunting adaptations. Their retractable claws, up to 1.5 inches long, enable grip during pursuits. Keen night vision allows them to hunt efficiently in low light. Strong jaws and sharp teeth ensure a powerful bite, critical for bringing down prey. Their social structure facilitates cooperative strategies, with lionesses coordinating to encircle and ambush targets like zebras. These adaptations ensure their status as formidable hunters within their ecosystem.
Habitat And Distribution
Lions primarily inhabit Africa’s savannas, where they thrive in open grasslands and sparse woodlands. These vast territories support large herbivore populations, essential for lion survival.
 African savannas provide lions with abundant prey, such as zebras and wildebeests, sustaining their populations. These ecosystems offer open landscapes that enable lions to utilize their keen eyesight and social hunting strategies effectively. The majority of lions reside in Sub-Saharan regions, particularly in countries like Tanzania, Botswana, and Kenya. Their distribution is influenced by prey availability, human activities, and environmental conditions.
African savannas provide lions with abundant prey, such as zebras and wildebeests, sustaining their populations. These ecosystems offer open landscapes that enable lions to utilize their keen eyesight and social hunting strategies effectively. The majority of lions reside in Sub-Saharan regions, particularly in countries like Tanzania, Botswana, and Kenya. Their distribution is influenced by prey availability, human activities, and environmental conditions.
Conservation areas play a crucial role in preserving lion populations. Protected zones like the Serengeti National Park and Kruger National Park offer refuge from threats like poaching and habitat encroachment. These areas help maintain biodiversity by safeguarding prey species and providing lions with stable habitats. In recent years, efforts to expand and connect protected areas have gained momentum, aiming to enhance genetic diversity and ensure long-term viability for lion populations. Conservationists continue to focus on mitigating human-lion conflicts and promoting coexistence initiatives.
King Of The Jungle
Lions hold a unique place in both the natural world and human culture, embodying strength and majesty. Their critical role in ecosystems and cultural symbolism underscores the urgency of conservation efforts. As apex predators, their survival is vital to maintaining ecological balance. Despite challenges like habitat loss and poaching, initiatives aimed at preserving their habitats and promoting coexistence offer hope. By continuing to support these efforts, future generations can appreciate the splendor and significance of lions in the wild. Their enduring presence not only enriches biodiversity but also inspires awe and respect across cultures worldwide.