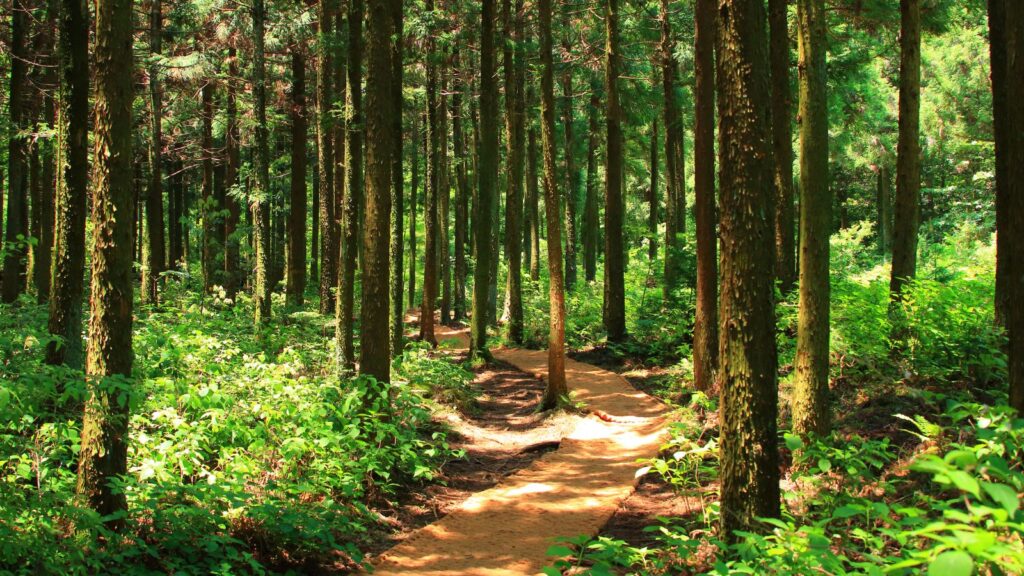
Fantasy:Ebecekxtpq8= Forest

Different types of forests exist, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests, each with distinct climatic conditions and biodiversity. Tropical rainforests, for example, thrive in warm regions with high rainfall, while boreal forests are found in colder areas, characterized by coniferous trees and harsh conditions.
Forests serve as carbon sinks, absorbing significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process helps mitigate climate change and maintains global carbon cycles. Additionally, forests play a key role in regulating water cycles, conserving soil, and offering resources for human use, such as timber, medicine, and food.
Forests also hold cultural importance for many indigenous communities who rely on them for their traditional lifestyles and practices. These ecosystems connect to the social, economic, and cultural fabric of human societies, offering spaces for recreation, spiritual practices, and scientific research.
Types Of Forests
Forests vary dramatically across the globe, each adapting to its environment. They provide unique ecosystems essential for biodiversity and ecological balance.
 Tropical forests, located near the Equator, boast high rainfall and warm temperatures year-round. These forests support immense biodiversity, including numerous insect species, exotic birds, and mammals like sloths and jaguars. They cover areas like the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, and Southeast Asia’s regions. Dense canopies dominate tropical forests, leading to a stratified structure that hosts various living organisms.
Tropical forests, located near the Equator, boast high rainfall and warm temperatures year-round. These forests support immense biodiversity, including numerous insect species, exotic birds, and mammals like sloths and jaguars. They cover areas like the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, and Southeast Asia’s regions. Dense canopies dominate tropical forests, leading to a stratified structure that hosts various living organisms.
Temperate forests exist in regions with distinct seasons and moderate rainfall. They spread across parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. These forests showcase a mix of deciduous and coniferous trees like oaks, maples, and pines. The changing seasons create a dynamic environment supporting diverse wildlife, including deer, foxes, and migratory birds. Leaf litter on the forest floor enriches the soil, supporting a robust understory.
Boreal forests, or taiga, stretch across the northern hemisphere within the subarctic zone. Characterized by cold temperatures and shorter growing seasons, they primarily consist of coniferous trees like spruces and firs. Covering vast areas in Canada, Russia, and Scandinavia, boreal forests play a crucial role in carbon storage and provide habitats for species adapted to harsh climates, such as lynxes, moose, and migratory birds. The dense network of trees and vast wetland areas supports unique ecosystems.
Importance Of Forests
Forests play a vital role in maintaining ecological stability and supporting life on Earth. Their extensive functions range from housing biodiversity to regulating climate conditions.
 Forests serve as critical habitats for over 80% of terrestrial species. They provide shelter and nourishment to countless organisms, from majestic tigers in tropical forests to migratory birds in temperate zones. The complex interdependence within forest ecosystems ensures a balance, where flora and fauna thrive collectively. Genetic diversity within these species aids adaptability and resilience, boosting overall ecosystem health.
Forests serve as critical habitats for over 80% of terrestrial species. They provide shelter and nourishment to countless organisms, from majestic tigers in tropical forests to migratory birds in temperate zones. The complex interdependence within forest ecosystems ensures a balance, where flora and fauna thrive collectively. Genetic diversity within these species aids adaptability and resilience, boosting overall ecosystem health.
Forests act as natural climate regulators by sequestering carbon dioxide. They absorb about 2.6 billion metric tons of CO2 annually, slowing global warming (Global Carbon Project, 2023). Through photosynthesis, forests transform carbon into biomass, reducing atmospheric carbon levels. They also modulate local climates by influencing temperature and precipitation patterns, acting as thermoregulators in both humid and arid regions.
Balancing Biodiversity
Forests are indispensable to the planet’s ecological health and human survival. They offer unmatched benefits, from mitigating climate change to supporting biodiversity and providing essential resources. However, the threats they face are significant and require immediate attention. Conservation efforts like reforestation and the establishment of protected areas are crucial in safeguarding these vital ecosystems. By prioritizing sustainable management and global cooperation, it’s possible to preserve forests for future generations, ensuring they continue to thrive and support life on Earth.