Animal:7ouud9bjbs0= Kola

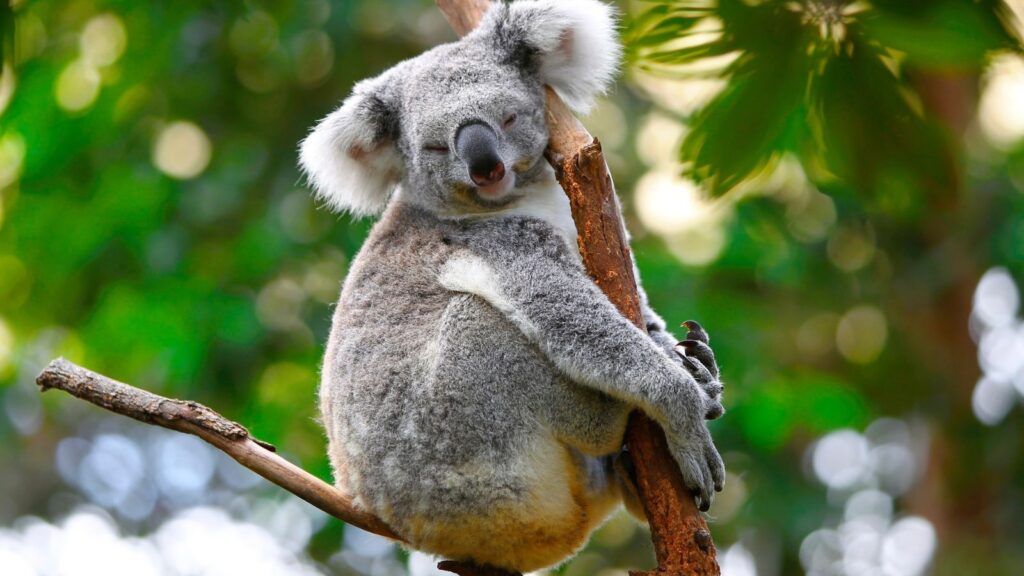
Physical characteristics of kola animals include a compact body and fur, ranging from brown to grey, which helps them blend into their surroundings. These mammals exhibit nocturnal behavior, being most active at night when they search for food. They rely on heightened senses to navigate their environment and locate nourishment.
Kola animals also hold an integral part in the food chain. They serve as prey for various rainforest predators, linking multiple trophic levels. As such, they contribute to biodiversity and ecological stability. Their role in the ecosystem underscores the importance of conservation efforts, which aim to protect their habitat and ensure their population thrives amidst environmental challenges.
Characteristics And Features
The kola animal exhibits distinct characteristics that enable survival and adaptation in rainforest habitats.
 Distinctive for its compact body, the kola animal sports fur that varies from brown to grey. This coloration provides excellent camouflage in the rainforest, aiding its ability to avoid predators. Equipped with sharp claws and a prehensile tail, it efficiently climbs trees, an essential skill for foraging and evading threats in dense forest canopies.
Distinctive for its compact body, the kola animal sports fur that varies from brown to grey. This coloration provides excellent camouflage in the rainforest, aiding its ability to avoid predators. Equipped with sharp claws and a prehensile tail, it efficiently climbs trees, an essential skill for foraging and evading threats in dense forest canopies.
The kola animal displays several unique traits contributing to its ecological role. As a nocturnal creature, it forages primarily at night using highly developed senses. Its diet, consisting of fruits, seeds, and insects, promotes seed dispersal and supports forest regeneration. These traits, alongside its role as prey for predators, establish the kola animal as a vital component in maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity.
Habitat And Distribution
The kola animal thrives in its natural environment, finding suitable conditions for survival in several regions of Africa.
Kola animals primarily inhabit tropical rainforests. These ecosystems offer dense canopies and a variety of food sources vital for their diet. Tall trees enable kola animals to exercise their climbing prowess, essential for both foraging and escaping predators. Additionally, the constant canopy cover provides protection from harsh weather conditions and potential hazards.
The geographic range of kola animals includes the dense rainforests of Central and West Africa. Countries like Gabon, Cameroon, and the Republic of the Congo host significant populations. These regions, characterized by rich biodiversity and ideal climatic conditions, support the survival and growth of kola animal populations, ensuring they remain a key component of their ecosystems.
Importance In Ecosystem
 The kola animal plays a crucial role in sustaining the rainforest ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal. As these animals forage for fruits and seeds, they inadvertently transport and deposit them across the forest floor, facilitating plant regeneration and maintaining biodiversity. Their activities ensure the continuous growth of various plant species, thereby supporting the habitat’s flora and fauna diversity.
The kola animal plays a crucial role in sustaining the rainforest ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal. As these animals forage for fruits and seeds, they inadvertently transport and deposit them across the forest floor, facilitating plant regeneration and maintaining biodiversity. Their activities ensure the continuous growth of various plant species, thereby supporting the habitat’s flora and fauna diversity.
In addition to plant population maintenance, kola animals serve as prey for larger predators, creating vital energy exchanges within the rainforest’s food web. This trophic linkage promotes ecological balance and supports predator populations that depend on them as a food source. By occupying this intermediary position, kola animals help stabilize the ecosystem, preventing any single species from dominating.
Kola animals also influence the forest structure. Their movement through the canopy helps trim foliage, allowing sunlight penetration to the forest floor.
Animal World
The kola animal’s significance in the rainforest ecosystem is undeniable, serving crucial roles in seed dispersal and maintaining biodiversity. Its unique adaptations and behaviors underscore its importance in ecological balance. Conservation efforts are essential to protect its habitat from threats like deforestation and illegal hunting.