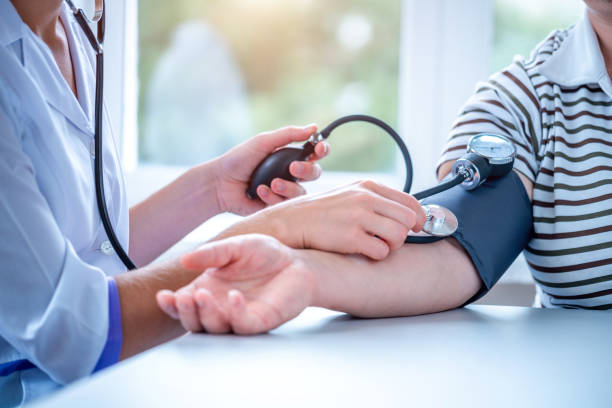
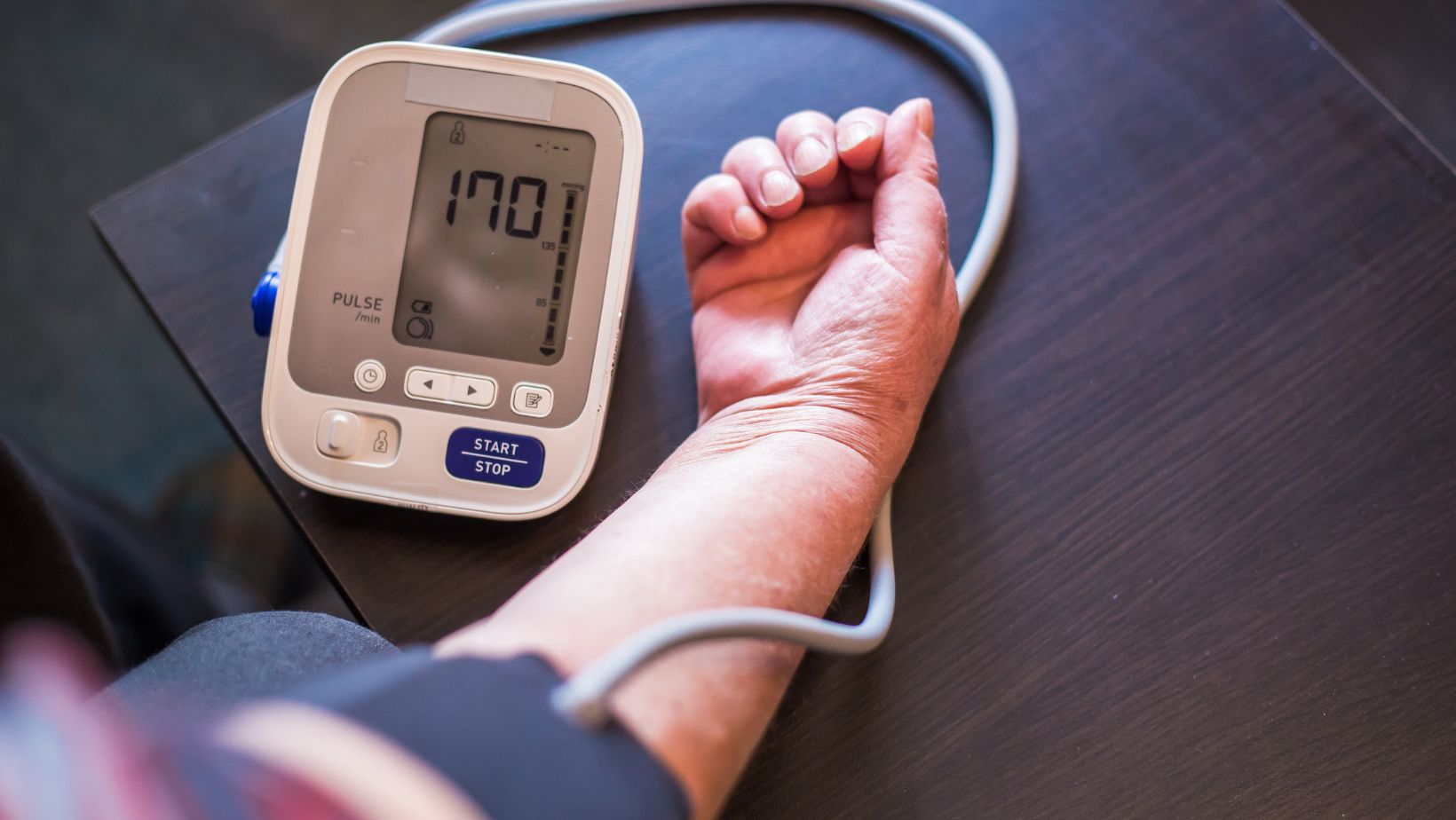
Hypertension—a leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease—affects millions worldwide. While prescription medications remain the cornerstone of treatment for many, interest in complementary and natural interventions is growing. These methods aim to address underlying causes of high blood pressure while promoting overall health. Recent advancements in nutrition science and lifestyle medicine offer promising avenues for managing blood pressure through innovative, natural strategies.
The Role of TMG in Cardiovascular Health
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has gained attention as a potential aid in cardiovascular health. TMG is critical in methylation, a biochemical process essential for cellular function. This compound is particularly effective in regulating homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to cardiovascular risk when elevated. Research suggests that lowering homocysteine may positively impact blood pressure and reduce arterial stiffness.
Dietary sources of TMG include beets, spinach and whole grains; however, TMG supplements can provide higher concentrations for those with specific cardiovascular health concerns. Studies have indicated that consistent TMG intake can support vascular health and improve blood flow, making it a valuable addition to a comprehensive blood pressure management plan. Its ability to enhance nitric oxide production further aids in relaxing blood vessels, contributing to healthy blood pressure levels.
The Impact of Diet and Nutrient Timing
The connection between diet and blood pressure is well-documented; emerging research highlights the importance of nutrient timing and meal composition in regulating blood pressure. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins remains a foundational guideline. However, integrating practices like intermittent fasting or time-restricted eating has shown additional benefits for some individuals.
Specific nutrients, such as potassium, magnesium and calcium are key in blood pressure regulation; potassium-rich foods like bananas, avocados and sweet potatoes help balance sodium levels in the body. Meanwhile, magnesium—found in nuts, seeds and leafy greens—supports vascular function while calcium contributes to healthy heart muscle contractions. These nutrients, when consumed in adequate amounts, create a synergistic effect that promotes optimal blood pressure control.
The Role of Physical Activity and Stress Reduction
Physical activity is a cornerstone of non-pharmacological blood pressure management. Regular exercise strengthens the cardiovascular system, improves arterial flexibility and reduces resting blood pressure—aerobic activities such as walking, swimming and cycling are particularly effective. Emerging evidence also highlights the benefits of resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) in reducing hypertension.
Chronic stress is another significant contributor to high blood pressure. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises and yoga have been shown to mitigate stress-induced blood pressure spikes. These practices activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing the physiological effects of stress. Consistent engagement in stress-reduction activities can result in measurable improvements in blood pressure and overall well-being.
Herbal and Nutraceutical Interventions
Several herbal and nutraceutical compounds have demonstrated potential in supporting healthy blood pressure. Hawthorn extract, for instance, has a long history of use in traditional medicine for cardiovascular health—modern studies suggest it may help dilate blood vessels and enhance heart function. Garlic extract is another well-researched natural remedy known for improving arterial elasticity and reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a powerful antioxidant that supports mitochondrial function and cardiovascular health. Research indicates that CoQ10 supplementation can lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish, have anti-inflammatory properties and promote vascular health, making them a valuable component of a blood pressure-focused nutritional strategy.
The Promise of Lifestyle Integration
Integrating multiple natural strategies creates a comprehensive approach to blood pressure management; combining dietary modifications, regular physical activity and targeted supplementation addresses the multifactorial nature of hypertension. Tracking progress through regular blood pressure monitoring and periodic health evaluations can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of these interventions.
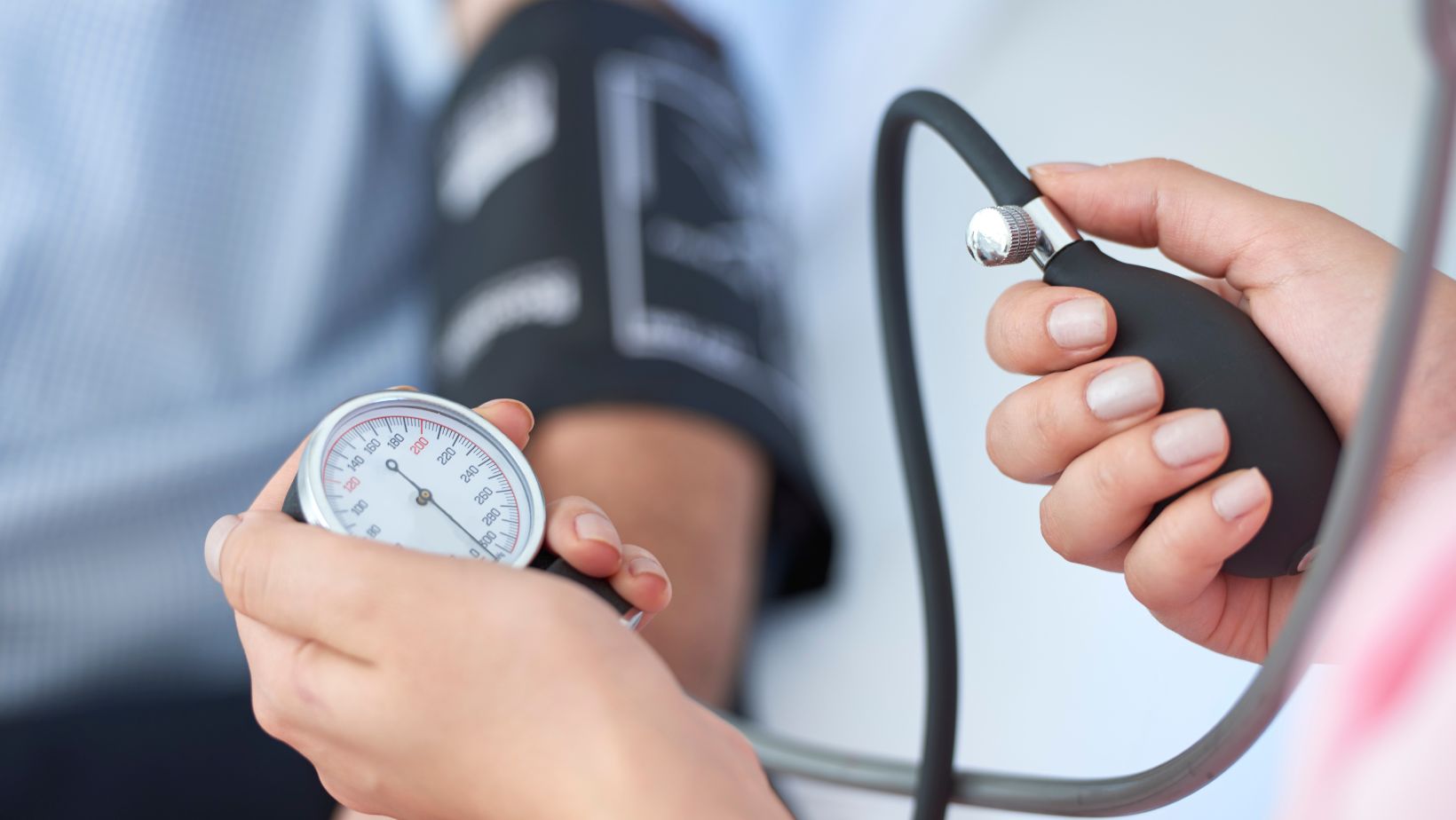

Advancements in wearable health technology have made it easier to measure vital signs and adherence to lifestyle changes. Devices that track blood pressure, heart rate and activity levels offer real-time feedback, empowering individuals to make informed decisions. These innovations, when combined with natural interventions, represent a paradigm shift in hypertension management.
Clinical Perspectives and Future Directions
Scientific research continues to explore the potential of natural interventions for blood pressure control. Large-scale clinical trials are evaluating the long-term effects of various supplements, diets and lifestyle changes. The integration of nutrigenomics—the study of how genetics influence nutrient metabolism—is establishing a pathway towards personalized approaches to hypertension management.
Although natural interventions offer significant promise, they are most effective when implemented alongside conventional medical care. Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients ensures that natural strategies complement—rather than replace—evidence-based treatments. As the understanding of hypertension evolves, innovative and integrative approaches are poised to redefine blood pressure management for diverse populations.